Is Mesima Right for You?
If you’re looking for a natural supplement that not only supports immunity but also enhances the effects of cancer treatment—Mesima may be the answer.
Thanks to its unique immune-regulating properties, Mesima is especially beneficial for those dealing with digestive system cancers or undergoing chemotherapy.

Clinically Proven Immune Support for Cancer Care
Mesima has been recognized as a clinical-grade immune modulator with strong anti-cancer benefits. Its ability to inhibit the growth of cancer cells, reduce chemotherapy side effects, and support overall treatment response has been verified through clinical research.
Notable institutions such as Saijo Central Hospital in Japan, Chungnam National University, Chonnam National University, Seoul National University, and Yonsei University in Korea have published clinical data validating Mesima’s benefits.
More Than Immunity:
Mesima’s Broader Clinical Impact
What sets Mesima apart from other mushroom extracts is not just its immune-boosting power, but its potential to prevent and manage chronic diseases such as metabolic syndrome and lifestyle-related disorders.
As a medicinal mushroom with pharmaceutical-grade immune-enhancing effects, Mesima combines traditional functional benefits with modern clinical value—making it an ideal supplement for those living in a high-stress, high-risk environment.
Clinical Case 1
Gastric Cancer: Long-Term Mesima Immunotherapy
Yamana Seizo, 西條病院, Published in Journal of Clinical & New Drugs, Japan (1988)
Patient
- 78-year-old male with terminal gastric cancer
- Cancer had spread throughout the stomach; surgery was not an option.
- Estimated survival at time of diagnosis: 2–3 months.
Treatment Protocol
Mesima: 2g per day (oral administration)
Clinical Outcomes
- Pain completely alleviated
- Maintained stable general condition
- No signs of cachexia or appetite loss
- 1 cm hepatic LDA disappeared; pulmonary tumor shadow resolved
- Patient passed away after 18 months due to a sudden gastrointestinal hemorrhage
→ Extended survival beyond initial prognosis; further survival was anticipated without hemorrhage.
Clinical Case 2
Immunochemotherapy Using Mesima After Gastric Cancer Surgery
Yamana Seizo, 西條病院, Published in Journal of Clinical & New Drugs, Japan (1990)
Subjects
22 patients diagnosed with Stage IV gastric cancer
- 10 patients underwent primary tumor resection
- 12 patients had exploratory laparotomy only
(non-resectable tumors)
Treatment Protocol
Mesima: 3g per day
Clinical Observations
- Increased appetite
- Reduced edema
- Weight gain
- Improved complexion
- Enhanced endothelial immune response
- Increased NK cell activity
Comparative Study
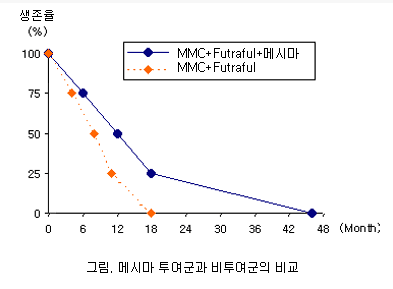
Survival data show that patients receiving Mesima alongside chemotherapeutic agents (mitomycin C and futraful) had prolonged survival compared to those who received chemotherapy alone.
NK Cell Activation
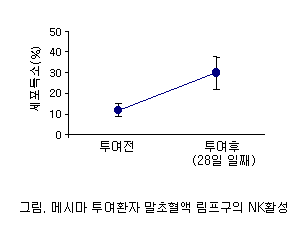
Peripheral blood NK cell activity (K-562 target, patient lymphocytes as effector) showed significant increase by day 28 of Mesima administration.
Clinical Case 3
Clinical Experience of Immuno-Mesima Polysaccharides in Advanced Cancer Patients
Yamana Seizo, 西條病院, Published in Journal of Clinical & New Drugs, Japan (1990)
Subjects
Total of 30 late-stage cancer patients
(16 males, 14 females)
- Gastric cancer: 6
- Lung cancer: 4
- Liver cancer: 6
- Esophageal cancer: 2
- Rectal cancer: 5
Mesima administered at 1–6g/day depending on patient condition
Clinical Outcomes
- Pain relief
- Improved appetite
- Stable body weight
- Improved motivation and quality of life
- Enhanced endothelial immune response
PHA and Con-A Lymphocyte Response

Mitogen-stimulated proliferation (PHA, Con-A) in Mesima-treated patients showed significantly improved lymphocyte response compared to untreated cancer patients, approaching levels seen in healthy controls.
Clinical Case 4
Postoperative Combination Therapy with Mesima and Chemotherapy in Gastric Cancer
Professor Hyun-Yong Chung, Chungnam National University College of Medicine, Presented at Japanese Society of Alternative Medicine (2000)
Subject
(Borrmann type III ulcerative lesion)
Treatment Protocol
- ostoperative Mesima: 3g/day
- Furtulon (doxifluridine): 600 mg/day orally, continued for 2+ years
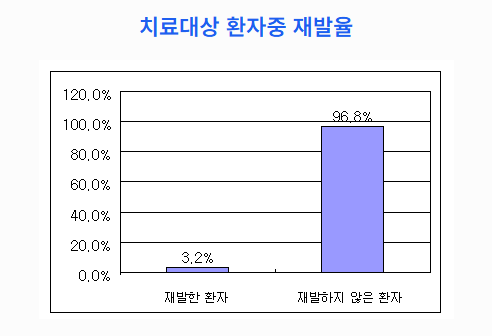
Clinical Outcomes
- Among 93 patients, only 3 (3.2%) experienced recurrence and died
- Remaining 90 patients showed stable conditions and continued therapy
- Evidence of liver metastasis suppression confirmed
Tumor Recurrence Rate in Treated Cases
Endoscopic Findings and Liver Metastasis Resolution
- Endoscopic imaging showed a lesion in the upper right area of the stomach.
- Follow-up investigations confirmed metastatic spread to the liver.
- After administration of Mesima, the metastatic tumor in the liver was no longer detectable.
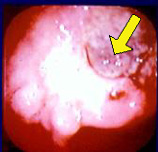
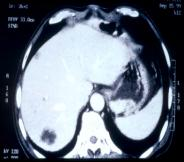

Case Observation
- 64-year-old male presented with hematemesis
- Endoscopy: Borrmann type III with thick blood clot at ulcer base (Photo 1)
- Preoperative lymph node metastasis observed
- Despite 3 rounds of adjuvant ELF chemotherapy, liver metastasis confirmed (Photo 2)
- After 4 cycles of cisplatin + 5-FU, Mesima and Furtulon were administered from March 2000
→ After 7 months, liver metastasis resolved (Photo 3) - Primary physician attributed the outcome to Mesima’s efficacy
Conclusion
- These findings suggest that Mesima is a safe and effective immunotherapeutic adjuvant post-surgery for gastric cancer.
- Particularly promising in suppressing liver metastases and reducing side effects when combined with chemotherapy,
- Mesima may contribute to developing safer, more effective integrative cancer therapies.
Clinical Case 5
Immunopotentiating Effects of Mesima (MesimaR) After Curative Gastrectomy in
Stage III Gastric Cancer Patients
Prof. Jin-Bok Kim, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Published in 대한암학회지, 1997
Subjects
40 patients with advanced gastric cancer who underwent curative gastrectomy
Treatment Groups
Group 1: Mesima-Ex 1g, three times daily after meals + Mitomycin-C (MMC) + 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU)
Group 2: Placebo (identical dosage form) + MMC + 5-FU
After Co-administration of Mesima with Chemotherapy Agents Mitomycin-C (MMC) and 5-FU
Patient Immune Recovery Capacity
Preoperative T3 Lymphocyte Baseline
Preoperative T4 Lymphocyte Baseline
T3 Lymphocyte Recovery Rate
T4 Lymphocyte Recovery Rate After 7 Months
Group 1: Mesima + MMC + 5-FU
88.90%
78.70%
Group 2: Placebo + MMC + 5-FU
63.50%
64.80%
Results
Patients in the Mesima group showed significantly higher recovery rates in total T lymphocytes and helper T cells (T4) compared to the placebo group.
Mesima combined with chemotherapy resulted in faster and more complete immune recovery.
Clinical Case 6
Antitumor Effects of Sanghwang (Mesima-Ex)
in Patients After Gastrectomy
for Advanced Gastric Adenocarcinoma
Prof. Joo-Hang Kim, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Published in 한국내과학회지, 1996
Subjects
67 patients with advanced gastric adenocarcinoma who had undergone gastrectomy
Treatment Groups
- Chemotherapy only: 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) + Adriamycin
- Combination therapy: 5-FU + Adriamycin + Mesima-Ex
Immunological Assessment
NK cell activity and Antibody-Dependent Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity (ADCC) were measured at 2 and 4 months post-treatment.
Results
In both time points, the group receiving Mesima-Ex with chemotherapy showed significantly higher NK cell and ADCC activity compared to the control group.
Conclusion
These findings demonstrate that Mesima’s immunopotentiating effects lead to enhanced in vivo immune responses.
Combined use of Mesima and chemotherapy after surgery resulted in better control of recurrence and improved therapeutic outcomes.
Comparison Between Mesima-Ex Group and Control Group at Treatment Initiation and After 4 Months
Immune Activity Comparison
Group
Treatment Group (N=30)
Control Group (N=37)
(%)
Natural Killer Cell Activity
Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity (ADCC)
Spontaneous Cytotoxic Activity
Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity (ADCC)
Baseline
26%
38.6%
28.1%
53%
2 months
28.9%
42.1%
27.3%
47.4%
Post-Gastrectomy Comparison Between Mesima-Ex Group and Control Group
Recurrence Suppression Rate
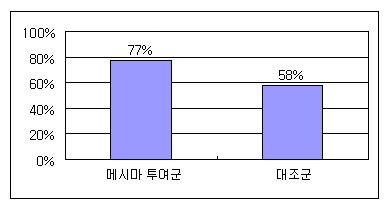
Recurrence Suppression
Abdominal CT scans revealed that recurrence occurred in only 23% of patients in the Mesima group, compared to the untreated group.
Clinical Case 7
of Mesima-Ex Acid
Prof. Sam-Yong Kim, Chungnam National University College of Medicine, Published in 대한암학회지, 1991
Subjects
22 terminal-stage cancer patients:
- Gastric cancer (9), liver cancer (3), colorectal cancer (2), unknown primary (2), other cancers (6)
- 16 males, 6 females
Treatment Regimens
A. Cyclophosphamide + Mesima-Ex Acid
→ Cyclophosphamide IV on day 1 + Mesima-Ex orally from day 4 to 17, repeated every 4 weeks
B. Combination with Chemotherapy
→ Mesima-Ex Acid 3g/day in 3 divided doses orally, alongside complex chemotherapy
Immune Function Results
Helper T cells (CD4) increased from 35.8±3.0% to 40.5±2.5%
CD4/CD5 ratio improved from 1.1±0.12 to 1.4±0.13
Lymphocyte proliferation (PHA): from 17,009±6,009 to 51,682±9,846 cpm
Stimulation index increased from 11.5±2.9 to 29.8±5.5
Summary of Clinical Response
- Of 15 patients tested for immune function, 12 (80%) showed improvement.
- Among 9 progressive cancer patients, 1 had partial response and 8 achieved stable disease.
- All 13 patients who received surgery or radiotherapy combined with Mesima-Ex Acid remained recurrence-free.
Conclusion
Mesima-Ex Acid demonstrated strong immunomodulatory effects with minimal side effects, and shows promising indirect anticancer efficacy across various cancer types.
